Define terminology related to the MAC & PHY
. . . .
Define terminology related to the MAC & PHY
MAC
MAC
- The data link layer is divided into 2 sub-layers
- The upper portion is the IEEE 802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC) sublayer
- The bottom portion of the Data-Link layer is the Media Access Control (MAC) sublayer
- MAC Service Data Unit
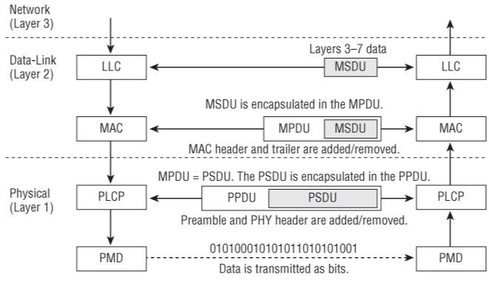
- When the Network layer (layer 3) sends data to the Data-Link layer,
- that data is handed off to the LLC and becomes known as the MAC
- Service Data Unit (MSDU).
- The MSDU contains data from the LLC and layers 3–7.
- A simple definition of the MSDU is that it is the data payload that contains the IP packet plus some LLC data.
- The 802.11-2012 standard states that the maximum size of the MSDU is 2,304 bytes.
- MAC Protocol Data Unit
- The LLC sublayer sends the MSDU to the MAC sublayer, the MAC header information is added to the MSDU to identify it.
- The MSDU is now encapsulated in a MAC Protocol Data Unit (MPDU).
- A simple definition of an 802.11 MPDU is that it is an 802.11 frame.
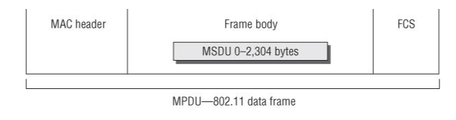
- As shown in Figure 9.1, an 802.11 MPDU consists of the following three basic components:
- MAC Header
- Frame control information, duration information, MAC addressing, and sequence control information are all found in the MAC header.
- Furthermore, QoS data frames contain specific QoS control information.
- Frame Body
- The frame body component can be variable in size and contains information that is different depending on the frame type and frame subtype.
- The MSDU upper layer payload is encapsulated in the frame body.
- The MSDU layer 3–7 payload is protected when using encryption.
- Frame Check Sequence (FCS)
- The FCS comprises a 32-bit cyclic-redundancy check (CRC) that is used to validate the integrity of received frames.
- At this point, the frame is ready to be passed onto the Physical layer, which will then further prepare the frame for transmission.
PHY
- The Physical layer is divided into 2 sub-layers
- The upper portion of the Physical layer is known as the Physical Layer Convergence Procedure (PLCP) sublayer
- The lower portion is known as the Physical Medium Dependent (PMD) sublayer.
- The PLCP prepares the frame for transmission by taking the frame from the MAC sublayer and creating the PLCP Protocol Data Unit (PPDU).
- The PMD sublayer then modulates and transmits the data as bits.
- PLCP Service Data Unit
- The PLCP Service Data Unit (PSDU) is a view of the MPDU from the
- Physical layer.
- The MAC layer refers to the frame as the MPDU, while the Physical layer refers to this same frame as the PSDU.
- The only difference is from which layer of the OSI model you are looking at the frame.
- PLCP Protocol Data Unit
- When the PLCP receives the PSDU, it then prepares the PSDU to be
- transmitted and creates the PLCP Protocol Data Unit (PPDU).
- The PLCP adds a preamble and PHY header to the PSDU.
- The preamble is used for synchronization between transmitting and receiving 802.11 radios.
- When the PPDU is created, the PMD sublayer takes the PPDU and modulates
- the data bits and begins transmitting.
- Figure 9.2 depicts a flowchart that shows the upper-layer information moving between the Data-Link and Physical layers.
Reference:
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
|
|