IEEE 802.11 Frame Format vs. IEEE 802.3 Frame Format
. . . .
IEEE 802.11 vs 802.3
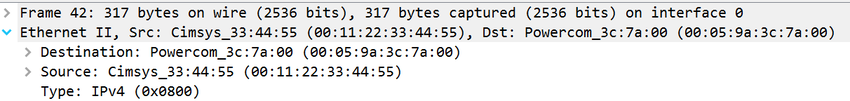
- One of the differences between 802.3 Ethernet and 802.11 wireless frames is the frame size.
- 802.3 frames have a maximum size of 1,518 bytes with a maximum data payload of 1,500 bytes
- If the 802.3 frames are 802.1Q tagged for VLANs and user priority, the maximum
size of the 802.3 frame is 1,522 bytes with a data payload of 1,504 bytes. - 802.11 frames are capable of transporting frames with an MSDU payload of 2,304 bytes of upper layer data.
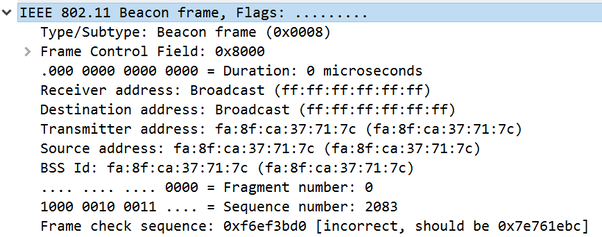
- MAC addressing used by 802.11 frames is much more complex than Ethernet frames.
- 802.3 frames have only a source address (SA) and destination address (DA) in the layer 2 header.
- 802.11 frames have up to four address fields in the MAC header.
- 802.11 frames typically use only three of the MAC address fields (4 in WDS environment).
Depending on whether the 802.11 traffic is upstream or downstream, the definition of each of the four MAC address fields in the layer 2 header will change.
The five definitions are as follows:
The five definitions are as follows:
- Source Address (SA) The MAC address of the original sending
station is known as the SA. The source address can originate from
either a wireless station or the wired network. - Destination Address (DA) The MAC address that is the final
destination of the layer 2 frame is known as the DA. The final
destination may be a wireless station or could be a destination on
the wired network such as a server or a router. - Transmitter Address (TA) The MAC address of an 802.11 radio
that is transmitting the frame onto the half-duplex 802.11
medium is known as the TA. - Receiver Address (RA) The MAC address of the 802.11 radio
that is intended to receive the incoming transmission from the
transmitting station is known as the RA. - Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID) This is the MAC address
that is the layer 2 identifier of the basic service set (BSS). The
BSSID is the MAC address of the AP’s radio or is derived from the
MAC address of the AP’s radio if multiple basic service sets exist.
Reference:
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
|
|