Reflection, refraction, diffraction, and scattering
. . . .
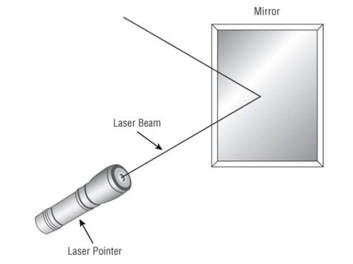
Reflection
When a wave hits a smooth object that is larger than the wave itself, depending on the media, the wave may bounce in another direction.
As a wave radiates from an antenna, it broadens and disperses. If portions of the wave are reflected, new wave fronts appear from the reflection points.
Causes
Outdoor:
Indoor:
Impact
Creates multipath, which can degrade the strength and quality of the received signal as well as cause data corruption or cancel signals.
The phase of the wave will be unchanged.
When a wave hits a smooth object that is larger than the wave itself, depending on the media, the wave may bounce in another direction.
As a wave radiates from an antenna, it broadens and disperses. If portions of the wave are reflected, new wave fronts appear from the reflection points.
Causes
Outdoor:
- Buildings
- Roads
- Bodies of water
- Earth’s surface
Indoor:
- Doors
- Walls
- File Cabinets
- Metal objects
- Glass
- Concrete
Impact
Creates multipath, which can degrade the strength and quality of the received signal as well as cause data corruption or cancel signals.
The phase of the wave will be unchanged.
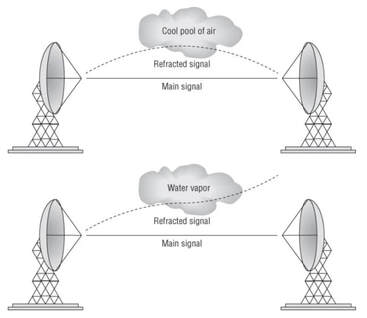
Refraction
Occurs when a RF signal is being bent. This typically can happen as the RF signal passes through a medium with a different density, thus causing the direction of the wave to change.
A change in refraction can typically appear when dealing with long-distance outdoor bridge links.
Refraction is measured based on the k-factor. A k-factor is simply a value to represent the bend that is occurring.
Causes
Outdoor:
Indoor:
Impact
May cause lower data rates, re-transmissions and lead to reduced capacity.
Occurs when a RF signal is being bent. This typically can happen as the RF signal passes through a medium with a different density, thus causing the direction of the wave to change.
A change in refraction can typically appear when dealing with long-distance outdoor bridge links.
Refraction is measured based on the k-factor. A k-factor is simply a value to represent the bend that is occurring.
- k-factor 1 = No bending
- k-factor <1 = Signal bending away from the earth
- k-factor >1 = Signal bending toward the earth
- k-factor 4/3 = Normal atmospheric conditions. Signal slightly bending toward the earth
Causes
Outdoor:
- Water vapor
- Changes in air temperature
- Changes in air pressure
Indoor:
- Certain types of glass
- Passing through various materials
Impact
May cause lower data rates, re-transmissions and lead to reduced capacity.
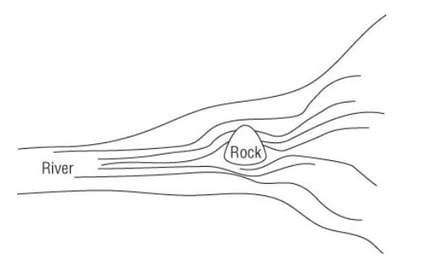
Diffraction
Diffraction is the bending and spreading around of an RF signal when it encounters an obstruction.
The waves that encounter the object bend around the object, taking a longer and different path.
The waves that do not encounter the object do not bend and maintain a shorter and original path.
Causes
Conditions that must be met for diffraction to occur.
Diffraction is caused by some sort of partial blockage such as a small hill or building that is between a transmitting radio and receiver.
Impact
RF shadow can occur causing dead coverage zones or receive degraded signals.
Diffraction is the bending and spreading around of an RF signal when it encounters an obstruction.
The waves that encounter the object bend around the object, taking a longer and different path.
The waves that do not encounter the object do not bend and maintain a shorter and original path.
Causes
Conditions that must be met for diffraction to occur.
- Characteristics of the obstructing object:
- Shape
- Size
- Material
- Characteristics of the RF signal:
- Polarization
- Phase
- Amplitude
Diffraction is caused by some sort of partial blockage such as a small hill or building that is between a transmitting radio and receiver.
Impact
RF shadow can occur causing dead coverage zones or receive degraded signals.
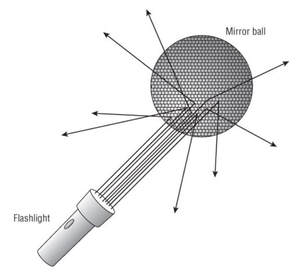
Scattering
Occurs when a signals wavelength is larger than pieces of a medium the signal is reflecting from or passing through.
Causes
Impact
RF encounters some type of uneven surface and is reflected into multiple directions. The main signal dissipates into multiple reflected signals causing substantial signal downgrade and may cause loss of received signal.
Occurs when a signals wavelength is larger than pieces of a medium the signal is reflecting from or passing through.
Causes
- Passing through substances:
- Smog
- Sandstorms
- Uneven surface:
- Chain link fences
- Wire mesh in stucco walls
- Tree foliage
- Rocky terrain
Impact
RF encounters some type of uneven surface and is reflected into multiple directions. The main signal dissipates into multiple reflected signals causing substantial signal downgrade and may cause loss of received signal.
Reference:
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
|
|