Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery (U-APSD)
. . . .
Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery (U-APSD)
- The main focus of the 802.11e amendment, which is now part of the 802.11-2012 standard, is quality of service.
- IEEE 802.11e amendment also introduced an enhanced power management method called automatic power save delivery (APSD):
- The two APSD methods that are defined are scheduled automatic power save delivery (S-APSD)
- Unscheduled automatic power save delivery (U-APSD).
- Wi-Fi Alliance’s WMM Power Save (WMM-PS) certification is based on U-APSD
- WMM-PS is an enhancement over the legacy power saving mechanisms already discussed.
- The goal of WMM-PS is to have client devices spend more time in a doze state and consume less power.
- WMM-PS is also designed to minimize latency for time-sensitive applications such as voice during the power-management process.
- The legacy power-management methods have several limitations.
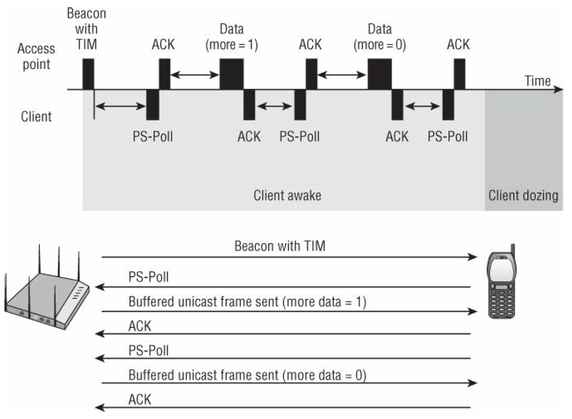
- As shown in Figure 9.12, a client using legacy power management must first wait for a beacon with a TIM before the client can request buffered unicast frames.
- The client must also send a unique PS-Poll frame to the AP to request every single buffered unicast frame.
- This ping-pong power-management method increases the latency of timesensitive
applications such as voice. - The clients must also stay awake during the ping-pong process, which results in reduced battery life.
- In addition, the amount of time that the clients spend dozing is determined by the vendor’s driver and not by the application traffic.
Reference:
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
|
|