Virtual carrier sense (NAV)
. . . .
Virtual carrier sense (NAV)
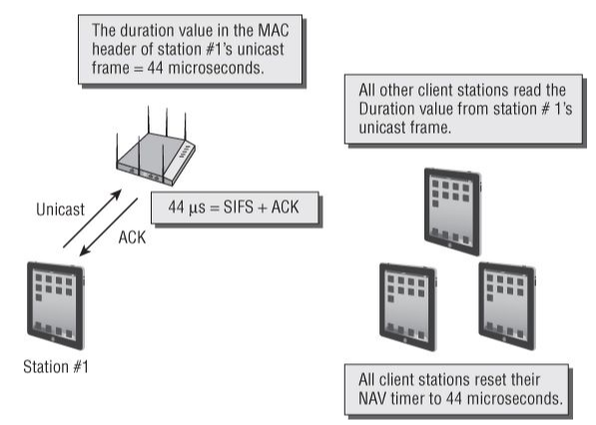
- Virtual carrier sense uses a timer mechanism known as the network allocation vector (NAV).
- The NAV timer maintains a prediction of future traffic on the medium based on Duration value information seen in a previous frame transmission.
- When an 802.11 radio is not transmitting, it is listening:
- When the listening radio hears a frame transmission from another station, it looks at the header of the frame and determines whether the Duration/ ID field contains a Duration value or an ID value.
- If the field contains a Duration value, the listening station will set its NAV timer to this value.
- The listening station will then use the NAV as a countdown timer, knowing that the RF medium should be busy until the countdown reaches 0.
- This process essentially allows the transmitting 802.11 radio to notify the other stations that the medium will be busy for a period of time (Duration/ ID value).
- The stations that are not transmitting listen and hear the Duration/ ID, set a countdown timer (NAV), and wait until their timer hits 0 before they can contend for the medium and eventually transmit on the medium.
- A station cannot contend for the medium until its NAV timer is 0, nor can a station transmit on the medium if the NAV timer is set to a nonzero value.
- Because the Duration/ ID value inside an 802.11 MAC header is used to set the NAV timer, virtual carrier sense is a layer 2 carrier sense mechanism.
Reference:
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
|
|