WMM Power-Save (WMM-PS)
. . . .
WMM Power-Save (WMM-PS)
- WMM Power Save (WMM-PS) helps conserve battery power for devices using Wi-Fi radios by managing the time the client device spends in sleep mode.
- Conserving battery life is critical for handheld devices such as barcode scanners and voice over Wi-Fi (VoWiFi) phones. To take advantage of power-saving capabilities, both the device and the access point must support WMM Power Save.
- The Wi-Fi Alliance’s WMM Power Save (WMM-PS) certification is based on U-APSD
- WMM-PS is an enhancement over the legacy power saving mechanisms
- WMM-PS uses a trigger mechanism to receive buffered unicast traffic based on WMM access categories.
- WMM access-category priority queues
- voice
- video
- best effort
- background
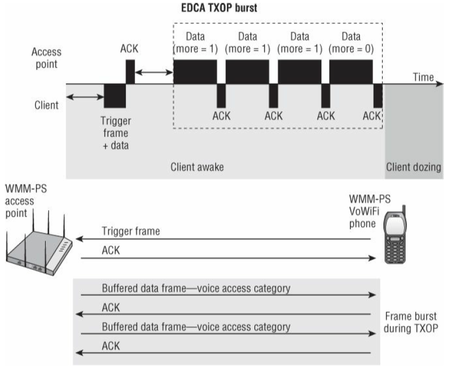
- As shown in Figure 9.13, the client station sends a trigger frame related to a WMM access category to inform the AP that the client is awake and ready to download any frames that the AP may have buffered for that access category.
- The trigger frame can also be an 802.11 data frame, thus eliminating the need for a separate PS-Poll frame.
- The AP will then send an ACK to the client and proceed to send a frame burst of buffered application traffic during a transmit opportunity (TXOP).
- The advantages of this enhanced power-management method include the following:
- Applications now control the power-save behavior by setting doze periods and sending trigger frames. VoWiFi phones will obviously send triggers to the AP frequently during voice calls, whereas a laptop radio using a data application will have a longer doze period.
- The trigger and delivery method eliminates the need for PS-Poll frames.
- The client can request to download buffered traffic and does not have to wait for a beacon frame.
- All the downlink application traffic is sent in a faster frame burst during the AP’s TXOP.
- Applications now control the power-save behavior by setting doze periods and sending trigger frames. VoWiFi phones will obviously send triggers to the AP frequently during voice calls, whereas a laptop radio using a data application will have a longer doze period.
- A couple of conditions have to be met for a Wi-Fi client to use the enhanced WMM-PS mechanisms:
- The client is Wi-Fi CERTIFIED for WMM-PS.
- The AP is Wi-Fi CERTIFIED for WMM-PS.
- The client is Wi-Fi CERTIFIED for WMM-PS.
- t should be noted that applications that do not support WMM-PS can still coexist with WMM Power Save–enabled applications. The data from the other applications will be delivered with legacy power-save methods.
Reference:
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
Coleman, David D.,Westcott, David A. CWNA: Certified Wireless Network Administrator Official Study Guide: Exam CWNA-106 Wiley.
|
|